In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), tongue diagnosis is one of the essential diagnostic methods, reflecting the body’s internal state and overall health. By examining the tongue’s color, shape, coating, and texture, TCM practitioners gain invaluable insights into a patient’s internal health patterns, guiding treatment plans effectively.
Understanding the Basics of Tongue Diagnosis
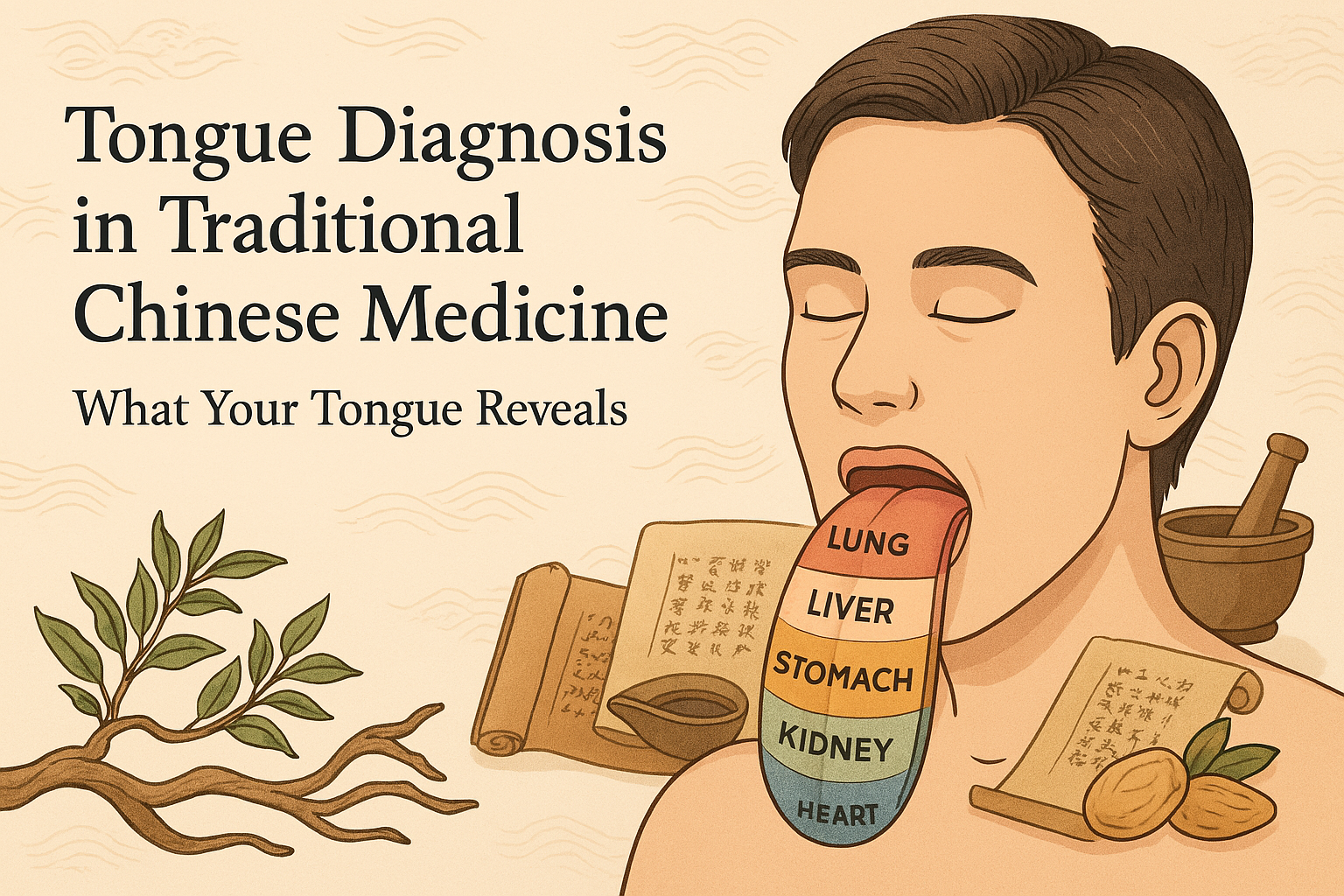
Tongue diagnosis is based on the theory that various areas of the tongue correspond to specific organs and bodily systems. For example:
- The tip of the tongue is associated with the Heart.
- The area just behind the tip relates to the Lungs.
- The tongue’s sides represent the Liver and Gallbladder.
- The center area connects to the Stomach and Spleen.
- The back corresponds to the Kidneys, Intestines, and Bladder.
Interpreting Tongue Colors
- Pale tongue: Suggests Qi, blood deficiency, or Yang deficiency (lack of warmth in the body).
- Red tongue: Indicates excessive heat or Yin deficiency, often associated with inflammation or internal heat.
- Purple tongue: Reflects poor blood circulation or blood stasis, potentially indicating chronic conditions.
Tongue Shape and Texture
- A swollen tongue may signify fluid retention or Spleen deficiency.
- A thin or shrunken tongue often indicates dehydration, Qi, or Yin deficiency.
- Teeth marks around the tongue’s edge typically suggest digestive weaknesses and dampness retention.
The Importance of Tongue Coating
The coating reflects the condition of the digestive system:
- A thin, white coating is normal and healthy.
- A thick white coating often suggests dampness or cold conditions.
- A yellow coating indicates heat and potential inflammation or infection.
- A greasy or sticky coating signals accumulated dampness or digestive disturbances.
Clinical Applications
TCM practitioners integrate tongue diagnosis into a comprehensive assessment, alongside pulse diagnosis, patient history, and physical examination. For example, a patient with chronic fatigue and digestive issues displaying a pale tongue with teeth marks and a thick white coating may be diagnosed with Spleen Qi deficiency and dampness. Treatments could include dietary recommendations, herbal medicine, and acupuncture targeting digestive functions.
Modern Perspectives and Validation
Modern medicine increasingly explores tongue diagnosis scientifically, using imaging and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to standardize diagnostic patterns. Clinical studies validate connections between tongue appearance and conditions like gastritis, anemia, and diabetes, highlighting its clinical relevance and potential for integration with conventional medicine.
Conclusion
Tongue diagnosis in TCM is a valuable, non-invasive diagnostic tool offering immediate insights into internal health. Its continued use in clinical practice and growing validation by modern research underline its significance and potential for broader acceptance in holistic healthcare.

发表回复